...
Climate NASA | Global Carbon Project | United Nations Framework Convention of Climate Change Newsroom
Latest News
Draft short paper on calculating the Method to Determine an Impact CDR Target that ought to be removed.
Reaching 1.5ºC will be challenging at best. Per Carbon Brief[1].Vox coverage on Green New Deal
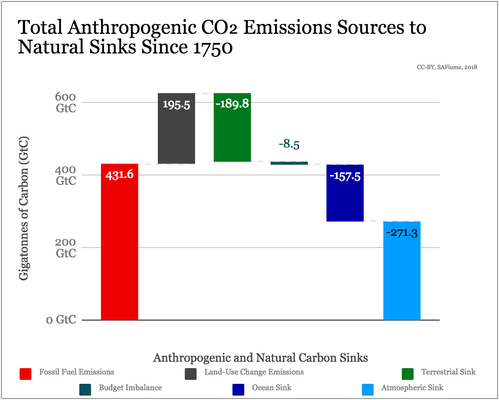
Every year the Global Carbon Budget releases progress on current atmospheric CO2 and GHGs levels. For 2017, peak carbon was pushed back, and 2% growth in carbon emissions projected. This year's (2017) carbon budget shows revised emissions from fossil fuels and land use. The new cumulative carbon from fossil fuel emissions (Eff) for 1870 to 2016 was 420 GtC and gained projected 10 GtC for 2017. This increases the total cumulative projection to about 430 GtC[2] from fossil fuel emissions, and not the 565 GtC as previously listed. Cumulative emissions from Land-use change was an additional 190GtC, bringing up total cumulative anthropogenic emissions from all human activity to 627GtC for 1750 to 20172018 emissions are projected to rise to a growth of 2% (projected 1.7% - 2.8%), after 2017 ended with 1.6% growth and 2016 was flat[2].
Global Carbon Budget 2017 Infographics2018 Infographics
Noteable Coverage
Vox: IPCC Special Report, and links this year's UNFCCC meeting: COP24.
Climate Change Exposé, New York Times: Loosing Earth: The Decade We Almost Stopped Climate Change
Forbes: Growth for Cleantech and Clean Energy Markets
Carbon Brief: Reaching 1.5ºC will be challenging at best.
Latest CO2 PPM
Atmospheric Anthropogenic Carbon to be Removed
How much Carbon do we need to remove? A rough estimate of is 500 Gt Carbon in two decades.Gt Carbon from emissions. This number shoots up close to 700 Gt Carbon if the Land Sink deteriorates. As of 2017, the total was 627 Gt Carbon.
| Iframe | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Note, we need to solidify carbon, in essence
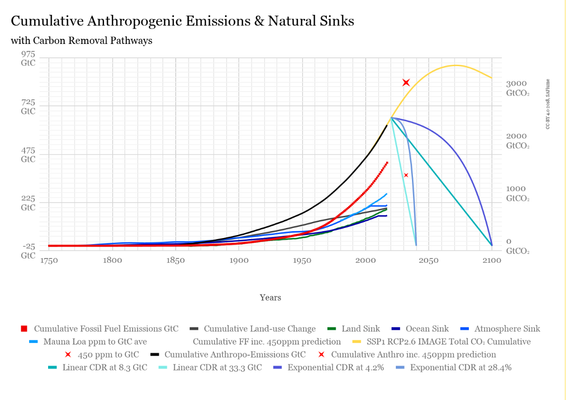
The red eXes are extrapolations of when we'd hit 450ppm from the light blue Mauna Loa ppm to GtC average curve. This assumes the current exponential growth rate continues unheeded till 450 ppm. 450ppm is projected to happen by 2032. The solid black line is the amount of fossil fuel emissions combined with land use change emissions which are projected to be in the atmosphere to cause 450 ppm.
Carbon Removal of the total cumulative emissions could look like the decline splines shown in teal or purple.
Note, to go a step beyond pure carbon-dioxide sequestration , to and fully remove carbon from the global carbon cycle and thereby , carbon can be solidified to stop it effecting from expediting climate change.
radiative forcing 3]
Exit Cryosphere Stability Zone
If one models global temperature and atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration (CO2 PPM) over the last 5M years using the Antarctic Vostok Ice Core data correlated to ice sheet existence, a large region emerges which includes data points starting with Northern Hemispheric Glaciation at about 2.7M years to just prior to the present. This data correlates a range of atmospheric CO2 concentration from 180 CO2 PPM[4] to sub 370 CO2 PPM[5] to temperatures that stay within a change of 2.5 Cº, over the last 2.7 M years. Outside of 2.7M years we observe higher temperatures and CO2 concentration and radically reduced Arctic ice sheet, glaciers, and radically raised ocean levels.[5] At present, Earth's climate is exceeding the previous stability zone due to increased global surface temperature and atmospheric CO2 concentration, leading to radical changes to global oceanic oscillations, and possible shutdown of thermohaline circulation[6] and increased reduction in polar ice sheets and further sea level rise. The shear fact that CO2 concentration has surpassed that during the Northern Hemispheric Glaciation point should raise great concern.
...
Image Credit: Assoc. Prof. Robert Cormia of Foothill College
...
All attempts should be made to quickly restore CO2 concentration as quickly as possible to 277 PPM[7] seen circa 1750 and additionally remove all of the anthropogenic fossil fuel emissions since 1750.
References
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Global Carbon Budget 2018 https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-10-2141-2018Anchor GCB2018 GCB2018
Global Carbon Budget 2017 https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-10-405-2018Anchor GCB2017 GCB2017
...